types of pump
Types[edit]
Mechanical pumps may be submerged in the fluid they are pumping or be placed external to the fluid.
Pumps can be classified by their method of displacement into electromagnetic pumps, positive-displacement pumps, impulse pumps, velocity pumps, gravity pumps, steam pumps and valveless pumps. There are three basic types of pumps: positive-displacement, centrifugal and axial-flow pumps. In centrifugal pumps the direction of flow of the fluid changes by ninety degrees as it flows over an impeller, while in axial flow pumps the direction of flow is unchanged.[2][3]
Electromagnetic pumps[edit]
An electromagnetic pump is a pump that moves liquid metal, molten salt, brine, or other electrically conductive liquid using electromagnetism.
A magnetic field is set at right angles to the direction the liquid moves in, and a current is passed through it. This causes an electromagnetic force that moves the liquid.
Applications include pumping molten solder in many wave soldering machines, pumping liquid-metal coolant, and magnetohydrodynamic drive.
Positive-displacement pumps[edit]

A positive-displacement pump makes a fluid move by trapping a fixed amount and forcing (displacing) that trapped volume into the discharge pipe.
Some positive-displacement pumps use an expanding cavity on the suction side and a decreasing cavity on the discharge side. Liquid flows into the pump as the cavity on the suction side expands and the liquid flows out of the discharge as the cavity collapses. The volume is constant through each cycle of operation.
Positive-displacement pump behavior and safety[edit]
Positive-displacement pumps, unlike centrifugal, can theoretically produce the same flow at a given speed (rpm) no matter what the discharge pressure. Thus, positive-displacement pumps are constant flow machines. However, a slight increase in internal leakage as the pressure increases prevents a truly constant flow rate.
A positive-displacement pump must not operate against a closed valve on the discharge side of the pump, because it has no shutoff head like centrifugal pumps. A positive-displacement pump operating against a closed discharge valve continues to produce flow and the pressure in the discharge line increases until the line bursts, the pump is severely damaged, or both.
A relief or safety valve on the discharge side of the positive-displacement pump is therefore necessary. The relief valve can be internal or external. The pump manufacturer normally has the option to supply internal relief or safety valves. The internal valve is usually used only as a safety precaution. An external relief valve in the discharge line, with a return line back to the suction line or supply tank provides increased safety.
Positive-displacement types[edit]
A positive-displacement pump can be further classified according to the mechanism used to move the fluid:
- Rotary-type positive displacement: internal or external gear pump, screw pump, lobe pump, shuttle block, flexible vane or sliding vane, circumferential piston, flexible impeller, helical twisted roots (e.g. the Wendelkolben pump) or liquid-ring pumps
- Reciprocating-type positive displacement: piston pumps, plunger pumps or diaphragm pumps
- Linear-type positive displacement: rope pumps and chain pumps
Rotary positive-displacement pumps[edit]

These pumps move fluid using a rotating mechanism that creates a vacuum that captures and draws in the liquid.[4]
Advantages: Rotary pumps are very efficient[5] because they can handle highly viscous fluids with higher flow rates as viscosity increases.[6]
Drawbacks: The nature of the pump requires very close clearances between the rotating pump and the outer edge, making it rotate at a slow, steady speed. If rotary pumps are operated at high speeds, the fluids cause erosion, which eventually causes enlarged clearances that liquid can pass through, which reduces efficiency.
Rotary positive-displacement pumps fall into five main types:
- Gear pumps – a simple type of rotary pump where the liquid is pushed around a pair of gears.
- Screw pumps – the shape of the internals of this pump is usually two screws turning against each other to pump the liquid
- Rotary vane pumps
- Hollow disc pumps (also known as eccentric disc pumps or hollow rotary disc pumps), similar to scroll compressors, these have an eccentric cylindrical rotor encased in a circular housing. As the rotor orbits, it traps fluid between the rotor and the casing, drawing the fluid through the pump. It is used for highly viscous fluids like petroleum-derived products, and it can also support high pressures of up to 290 psi.[7][8][9][10][11][12][13]
- Peristaltic pumps have rollers which pinch a section of flexible tubing, forcing the liquid ahead as the rollers advance. Because they are very easy to keep clean, these are popular for dispensing food, medicine, and concrete.
Reciprocating positive-displacement pumps[edit]
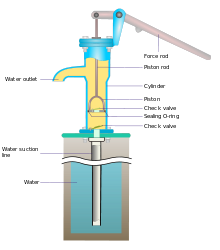

Reciprocating pumps move the fluid using one or more oscillating pistons, plungers, or membranes (diaphragms), while valves restrict fluid motion to the desired direction. In order for suction to take place, the pump must first pull the plunger in an outward motion to decrease pressure in the chamber. Once the plunger pushes back, it will increase the chamber pressure and the inward pressure of the plunger will then open the discharge valve and release the fluid into the delivery pipe at constant flow rate and increased pressure.
Pumps in this category range from simplex, with one cylinder, to in some cases quad (four) cylinders, or more. Many reciprocating-type pumps are duplex (two) or triplex (three) cylinder. They can be either single-acting with suction during one direction of piston motion and discharge on the other, or double-acting with suction and discharge in both directions. The pumps can be powered manually, by air or steam, or by a belt driven by an engine. This type of pump was used extensively in the 19th century—in the early days of steam propulsion—as boiler feed water pumps. Now reciprocating pumps typically pump highly viscous fluids like concrete and heavy oils, and serve in special applications that demand low flow rates against high resistance. Reciprocating hand pumps were widely used to pump water from wells. Common bicycle pumps and foot pumps for inflation use reciprocating action.
These positive-displacement pumps have an expanding cavity on the suction side and a decreasing cavity on the discharge side. Liquid flows into the pumps as the cavity on the suction side expands and the liquid flows out of the discharge as the cavity collapses. The volume is constant given each cycle of operation and the pump's volumetric efficiency can be achieved through routine maintenance and inspection of its valves.[14]
Typical reciprocating pumps are:
- Plunger pumps – a reciprocating plunger pushes the fluid through one or two open valves, closed by suction on the way back.
- Diaphragm pumps – similar to plunger pumps, where the plunger pressurizes hydraulic oil which is used to flex a diaphragm in the pumping cylinder. Diaphragm valves are used to pump hazardous and toxic fluids.
- Piston pumps displacement pumps – usually simple devices for pumping small amounts of liquid or gel manually. The common hand soap dispenser is such a pump.
- Radial piston pumps - a form of hydraulic pump where pistons extend in a radial direction.
- Vibratory pumps or vibration pumps - a particularly low-cost form of plunger pump, popular in low-cost espresso machines.[15][16] The only moving part is a spring-loaded piston, the armature of a solenoid. Driven by half-wave rectified alternating current, the piston is forced forward while energized, and is retracted by the spring during the other half cycle. Due to their inefficiency, vibratory pumps typically cannot be operated for more than one minute without overheating, so are limited to intermittent duty.
Various positive-displacement pumps[edit]
The positive-displacement principle applies in these pumps:
- Rotary lobe pump
- Progressing cavity pump
- Rotary gear pump
- Piston pump
- Diaphragm pump
- Screw pump
- Gear pump
- Hydraulic pump
- Rotary vane pump
- Peristaltic pump
- Rope pump
- Flexible impeller pump
Gear pump[edit]
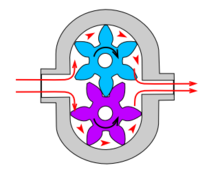
This is the simplest form of rotary positive-displacement pumps. It consists of two meshed gears that rotate in a closely fitted casing. The tooth spaces trap fluid and force it around the outer periphery. The fluid does not travel back on the meshed part, because the teeth mesh closely in the center. Gear pumps see wide use in car engine oil pumps and in various hydraulic power packs.

Comments
Post a Comment